Is Silymarin Powder Effective in Managing Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), has become a growing health concern worldwide. As researchers and healthcare professionals seek effective management strategies, attention has turned to natural compounds with potential hepatoprotective properties. Among these, silymarin powder, derived from milk thistle (Silybum marianum), has garnered significant interest. This powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent has shown promise in addressing the underlying mechanisms of fatty liver disease. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the efficacy of silymarin powder in managing fatty liver disease, examining its mechanisms of action, clinical evidence, and potential as a natural therapeutic option. By understanding the role of silymarin powder in liver health, we can better assess its value in the treatment and prevention of fatty liver disease, offering hope for those affected by this increasingly prevalent condition.
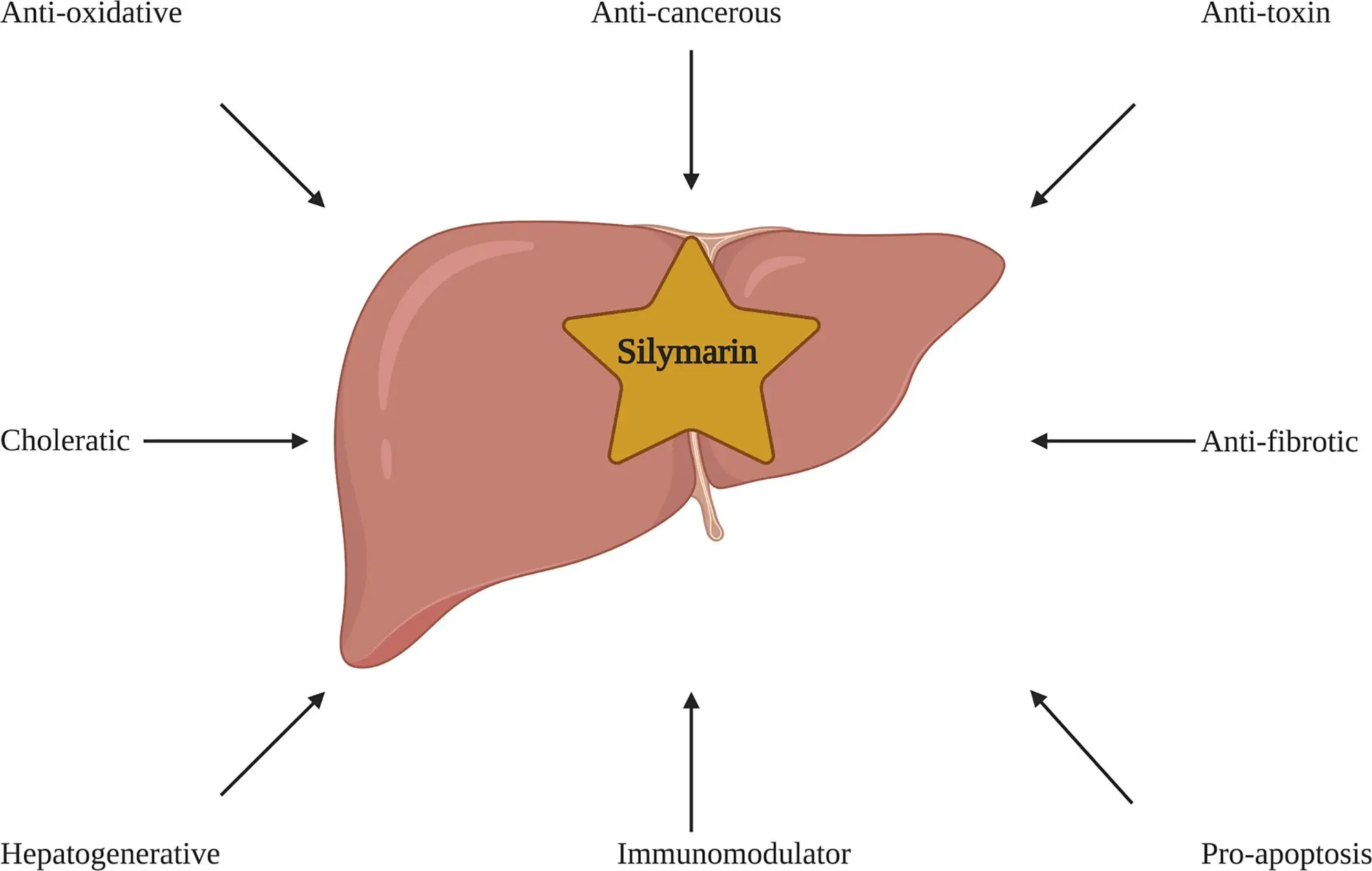
Exploring the Hepato-protective Mechanisms: How Silymarin Powder Reduces Liver Fat and Inflammation
Antioxidant Properties and Free Radical Scavenging
Silymarin powder, derived from milk thistle, exhibits potent antioxidant properties that play a crucial role in protecting liver cells from oxidative stress. The active compounds in silymarin, particularly silybin, act as powerful free radical scavengers, neutralizing harmful molecules that can damage cellular structures. By reducing oxidative stress, silymarin powder helps prevent lipid peroxidation, a process that contributes to the accumulation of fat in liver cells. This antioxidant action is fundamental to silymarin's ability to combat fatty liver disease, as it interrupts the cycle of inflammation and cellular damage that perpetuates the condition. Furthermore, the antioxidant effects of silymarin powder extend beyond the liver, offering systemic benefits that support overall health and potentially mitigate risk factors associated with fatty liver disease.
Anti-inflammatory Effects on Liver Tissue
Inflammation is a key driver in the progression of fatty liver disease, and silymarin powder demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory properties that can help mitigate this process. The flavonolignans in silymarin powder, particularly silybin, have been shown to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduce the activation of inflammatory pathways in liver cells. By modulating the inflammatory response, silymarin powder helps to break the cycle of chronic inflammation that contributes to liver damage and fibrosis. This anti-inflammatory action is particularly beneficial in cases of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and cellular damage. The ability of silymarin powder to reduce inflammation not only helps to alleviate symptoms but also potentially slows the progression of liver disease, making it a valuable component in comprehensive management strategies for fatty liver conditions.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism and Fat Accumulation
One of the key mechanisms by which silymarin powder addresses fatty liver disease is through its effects on lipid metabolism. Research has shown that silymarin can influence the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown, potentially reducing the accumulation of triglycerides in liver cells. Silymarin powder has been observed to enhance the activity of enzymes responsible for fatty acid oxidation, promoting the breakdown of excess fat in the liver. Additionally, it may help regulate insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, factors that are closely tied to the development and progression of fatty liver disease. By modulating these metabolic processes, silymarin powder contributes to a reduction in liver fat content, addressing one of the primary features of fatty liver disease. This multi-faceted approach to lipid metabolism makes silymarin powder a promising natural intervention for managing and potentially reversing the effects of fatty liver accumulation.
Reviewing Clinical Evidence and Human Studies on Silymarin's Efficacy for NAFLD and NASH
Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Several randomized controlled trials have investigated the efficacy of silymarin powder in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). These studies have provided valuable insights into the potential benefits of silymarin supplementation. In one notable trial, patients with NAFLD who received silymarin powder showed significant improvements in liver enzyme levels, particularly ALT and AST, compared to those receiving a placebo. Another study focusing on NASH patients demonstrated that silymarin powder, when combined with lifestyle modifications, led to greater reductions in liver fat content as measured by imaging techniques. These controlled trials have also explored various dosages and durations of silymarin powder supplementation, helping to establish optimal treatment protocols. While results have been generally positive, it's important to note that some studies have shown mixed outcomes, highlighting the need for further research to fully understand the efficacy of silymarin powder across different patient populations and stages of liver disease.
Long-term Effects and Safety Profile in Human Subjects
The long-term effects and safety profile of silymarin powder in human subjects with fatty liver disease have been subjects of ongoing research. Studies examining extended use of silymarin powder have generally reported favorable safety profiles, with minimal side effects reported even at higher doses. Long-term studies have shown that continued use of silymarin powder may lead to sustained improvements in liver function tests and markers of liver health. Some research has also suggested potential benefits in reducing the risk of progression from NAFLD to more severe forms of liver disease, although more longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these findings. The safety of silymarin powder is further supported by its long history of use in traditional medicine and its generally well-tolerated nature. However, as with any supplement, individual responses can vary, and some patients may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort. Overall, the cumulative evidence from human studies indicates that silymarin powder is a safe option for long-term use in managing fatty liver disease, with ongoing research continuing to refine our understanding of its long-term efficacy and potential preventive benefits.
Biomarkers and Imaging Results in Clinical Studies
Clinical studies evaluating the efficacy of silymarin powder in fatty liver disease have relied on various biomarkers and imaging techniques to assess its impact. Liver enzyme levels, particularly ALT and AST, are commonly used as indicators of liver health and have shown consistent improvements in patients taking silymarin powder. More advanced biomarkers, such as markers of oxidative stress and inflammation, have also been examined in some studies, often showing positive changes with silymarin supplementation. Imaging techniques, including ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), have been employed to directly visualize changes in liver fat content and structure. Several studies using these imaging modalities have reported reductions in liver fat and improvements in liver texture following silymarin powder treatment. Additionally, non-invasive tests like the Fatty Liver Index (FLI) and NAFLD fibrosis score have been utilized to assess the overall impact of silymarin on liver health. While these biomarkers and imaging results provide valuable insights, researchers continue to explore more sensitive and specific measures to fully capture the effects of silymarin powder on fatty liver disease progression and reversal.
Comparing Silymarin Powder as a Natural Antioxidant Therapy to Conventional Liver Support
Advantages of Silymarin Over Synthetic Pharmaceuticals
Silymarin powder offers several advantages over synthetic pharmaceuticals in the management of fatty liver disease. As a natural compound, silymarin is generally well-tolerated and associated with fewer side effects compared to many synthetic drugs. Its multi-faceted mechanism of action, encompassing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic effects, provides a comprehensive approach to liver health that many single-target pharmaceuticals lack. Silymarin powder's ability to address multiple aspects of liver dysfunction makes it a versatile option for patients at various stages of fatty liver disease. Additionally, the long history of milk thistle use in traditional medicine provides a wealth of anecdotal evidence supporting its safety and efficacy. Unlike some synthetic drugs that may strain the liver, silymarin powder is hepatoprotective, potentially offering benefits beyond just treating fatty liver disease. Its natural origin also makes it an attractive option for patients seeking more holistic or integrative approaches to their health care. However, it's important to note that while silymarin powder shows promise, it should not be considered a replacement for prescribed medications without consulting a healthcare professional.
Potential Synergistic Effects with Lifestyle Interventions
One of the key strengths of silymarin powder in managing fatty liver disease is its potential for synergistic effects when combined with lifestyle interventions. Studies have shown that silymarin supplementation can enhance the benefits of dietary changes and increased physical activity in patients with NAFLD and NASH. For instance, patients adopting a healthy diet and exercise regimen while taking silymarin powder have demonstrated more significant improvements in liver enzyme levels and fat reduction compared to those using lifestyle modifications alone. The antioxidant properties of silymarin powder may complement the metabolic improvements achieved through diet and exercise, creating a more robust defense against liver damage. Additionally, some research suggests that silymarin powder may help mitigate the oxidative stress associated with rapid weight loss, which can sometimes exacerbate liver inflammation. This synergistic approach not only addresses the physiological aspects of fatty liver disease but also supports patients in maintaining long-term lifestyle changes, potentially leading to more sustainable health improvements. The combination of silymarin powder with lifestyle interventions represents a holistic approach to liver health that aligns well with current recommendations for NAFLD and NASH management.
Cost-effectiveness and Accessibility Considerations
When comparing silymarin powder to conventional liver support treatments, cost-effectiveness and accessibility are important factors to consider. Silymarin powder, derived from the readily available milk thistle plant, is generally more affordable than many prescription medications used for liver support. This cost advantage makes it a more accessible option for long-term management of fatty liver disease, particularly for patients without comprehensive health insurance coverage. The availability of silymarin powder as a dietary supplement also means it can be purchased without a prescription, potentially increasing access for those who might face barriers to regular medical care. However, it's crucial to note that the quality and potency of silymarin powder can vary between manufacturers, and consumers should choose reputable sources to ensure they are getting a standardized, high-quality product. While the initial cost of high-quality silymarin powder may be higher than some generic supplements, its potential to prevent progression of liver disease and reduce the need for more expensive interventions in the future could make it a cost-effective option in the long run. As research continues to support the efficacy of silymarin powder, it may become an increasingly attractive option for both patients and healthcare systems looking to manage the growing burden of fatty liver disease effectively and economically.
Conclusion
Silymarin powder shows promising potential in managing fatty liver disease, offering a natural, multi-faceted approach to liver health. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic-modulating properties make it a valuable tool in combating NAFLD and NASH. While clinical evidence is encouraging, more research is needed to fully establish its long-term efficacy and optimal usage. As a complementary therapy alongside lifestyle interventions, silymarin powder presents a safe, cost-effective option for those seeking to improve liver health. However, it's crucial to consult healthcare professionals before incorporating silymarin powder into any treatment regimen, ensuring its appropriate use in individual cases of fatty liver disease.
At Avans NutriHealth Co., Ltd., we are committed to providing high-quality silymarin powder and other plant extracts to support your health and wellness goals. As a leading manufacturer and supplier in China, we offer a range of nutritional supplements, food additives, and cosmetic ingredients backed by rigorous quality control and innovative research. Our team of experts is dedicated to delivering exceptional products and personalized solutions to meet your specific needs. With certifications including ISO, USDA, HACCP, and FSSC22000, we ensure the highest standards of safety and efficacy in all our offerings. For more information on our silymarin powder and other products, please contact us at Lillian@avansnutri.com. Choose Avans NutriHealth for a trusted partner in your journey towards better health and wellness.
FAQ
Q: What is the recommended dosage of silymarin powder for fatty liver disease?
A: The optimal dosage can vary, but most studies have used 420-800 mg of silymarin per day, divided into 2-3 doses. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Q: How long does it take to see results from silymarin powder supplementation?
A: Results can vary, but some studies have shown improvements in liver enzymes within 8-12 weeks of consistent use. Long-term benefits may take several months to become apparent.
Q: Can silymarin powder be taken alongside other medications for liver health?
A: While generally safe, silymarin can interact with certain medications. It's crucial to consult with your doctor before combining silymarin powder with other liver treatments or medications.
Q: Are there any side effects associated with silymarin powder?
A: Silymarin is generally well-tolerated, but some people may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort. Allergic reactions are rare but possible, especially in those allergic to plants in the same family as milk thistle.
Q: Is silymarin powder effective for all types of fatty liver disease?
A: Silymarin has shown benefits for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Its effectiveness may vary depending on the severity and cause of the liver condition.
References
1. Abenavoli, L., et al. (2018). Milk thistle (Silybum marianum): A concise overview on its chemistry, pharmacological, and nutraceutical uses in liver diseases. Phytotherapy Research, 32(11), 2202-2213.
2. Gillessen, A., & Schmidt, H. H. (2020). Silymarin as supportive treatment in liver diseases: A narrative review. Advances in Therapy, 37(4), 1279-1301.
3. Karimi, G., et al. (2011). Silymarin, a promising pharmacological agent for treatment of diseases. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 14(4), 308-317.
4. Loguercio, C., & Festi, D. (2011). Silybin and the liver: From basic research to clinical practice. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 17(18), 2288-2301.
5. Saller, R., et al. (2008). The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs, 68(1), 85-100.
6. Zhong, S., et al. (2017). The therapeutic effect of silymarin in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty disease: A meta-analysis (PRISMA) of randomized control trials. Medicine, 96(49), e9061.